Data preparation: Difference between revisions
m 42 revision |
|||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Prepare Data for XML Transfer and ABCD Mapping = | |||
Before you start with data preparation [http://wiki.bgbm.org/bps/index.php/Preparation as described in BioCASE documentation], it is necessary to prepare the content of the data set for following reasons: | |||
Before you start with data preparation | |||
it is | |||
* Make content information comprehensible | * Make content information comprehensible | ||
* Add fields mandatory to ABCD Mapping | * Add fields mandatory to ABCD Mapping | ||
== | The following '''preparation steps''' are recommended: | ||
===Convert abbreviations into complete words=== | |||
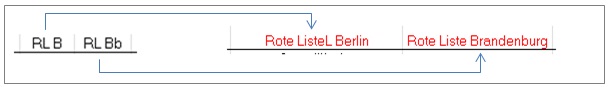
In the screenshot below abbreviations in original data on the left were transferred to complete words in the right: RLB - Rote Liste Berlin (= Red Lists Berlin), RLBb - Rote Liste Brandenburg (= Red Lists Brandenburg) | In the screenshot below abbreviations in original data on the left were transferred to complete words in the right: RLB - Rote Liste Berlin (= Red Lists Berlin), RLBb - Rote Liste Brandenburg (= Red Lists Brandenburg) | ||
[[File:ResolveAbbreviations.jpg]] | [[File:ResolveAbbreviations.jpg]] | ||
== | ===Translate numbers or characters into text=== | ||
In some cases numbers or characters don’t represent a value but qualitative statements. To make this information comprehensible it is recommended | In some cases numbers or characters don’t represent a value but are qualitative statements. To make this information comprehensible it is recommended that they are converted into written text. | ||
You can use “if functions” in Excel for conversion of numbers and characters. | You can use “if functions” in Excel for conversion of numbers and characters. | ||
e.g. =IF(A3="3";"3-gefährdet";IF(A3="1";"1- vom Aussterben bedroht";A3;"")) | |||
==== '''Conversion of numbers'''==== | |||
When only numbers where present in the original data, a textual description was added to define the number. These were as follows: | |||
*1 – vom Aussterben bedroht (= critically endangered) | |||
*2 – stark gefährded (= endangered) | |||
*3 – gefährdet (= vulnerable) | |||
*4 - potentiell gefährdet (= near threatended) | |||
[[File:TranslateNumbersintoText.JPG]] | |||
==== '''Conversion of characters'''==== | |||
Characters in original data were converted to text (for different ecological types) | |||
[[File:TranslateCharacterssintoText.JPG]] | |||
===Convert Values into the ABCD essential form=== | |||
* Example: Transform lat/lon coordinates into decimal form (required for ABCD). | |||
Latitude in degree, minute and seconds were transformed into decimal degrees. | |||
[[File:ConvertValues.JPG]] | |||
== | ===Add columns with ‘unit of measurement’=== | ||
Otherwise in ABCD the units cannot be allocated to the values correctly. | Add columns with ‘unit of measurement’, if missing, according to the measurement. Otherwise in ABCD the units cannot be allocated to the values correctly. | ||
*Example: header of a column in Excel: tarsus (mm) – length, width, height. Add columns with header ‘Unit’ and enter ‘mm’ in every row. | |||
You can add repeated data values to columns in MS Access with by using following SQL statement: SELECT [unit_tarsus_length] AS mm | |||
[[File:AddUnitOfMeasurement.JPG]] | |||
===Add core information from metadata=== | |||
Add core information from metadata to every unit, if missing in the unit table. You can add this information by using the SQL statement above. | |||
== | ===Denormalise information=== | ||
In the case of repeatable elements in ABCD you need to denormalise the data. | |||
For more information see the [http://wiki.bgbm.org/bps/index.php/Preparation BioCASE documention Wiki] - under the section "Controlled Denormalisation". | |||
== | ===ABCD Mapping=== | ||
Each column in the prepared dataset should be mapped to an ABCD element using the [http://wiki.bgbm.org/bps BioCase Provider software]. There is a tutorial describing each step in the mapping under the section '''ABCD Mapping'''. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:15, 10 November 2014
Prepare Data for XML Transfer and ABCD Mapping
Before you start with data preparation as described in BioCASE documentation, it is necessary to prepare the content of the data set for following reasons:
- Make content information comprehensible
- Add fields mandatory to ABCD Mapping
The following preparation steps are recommended:
Convert abbreviations into complete words
In the screenshot below abbreviations in original data on the left were transferred to complete words in the right: RLB - Rote Liste Berlin (= Red Lists Berlin), RLBb - Rote Liste Brandenburg (= Red Lists Brandenburg)
Translate numbers or characters into text
In some cases numbers or characters don’t represent a value but are qualitative statements. To make this information comprehensible it is recommended that they are converted into written text. You can use “if functions” in Excel for conversion of numbers and characters. e.g. =IF(A3="3";"3-gefährdet";IF(A3="1";"1- vom Aussterben bedroht";A3;""))
Conversion of numbers
When only numbers where present in the original data, a textual description was added to define the number. These were as follows:
- 1 – vom Aussterben bedroht (= critically endangered)
- 2 – stark gefährded (= endangered)
- 3 – gefährdet (= vulnerable)
- 4 - potentiell gefährdet (= near threatended)
Conversion of characters
Characters in original data were converted to text (for different ecological types)
Convert Values into the ABCD essential form
- Example: Transform lat/lon coordinates into decimal form (required for ABCD).
Latitude in degree, minute and seconds were transformed into decimal degrees.
Add columns with ‘unit of measurement’
Add columns with ‘unit of measurement’, if missing, according to the measurement. Otherwise in ABCD the units cannot be allocated to the values correctly.
- Example: header of a column in Excel: tarsus (mm) – length, width, height. Add columns with header ‘Unit’ and enter ‘mm’ in every row.
You can add repeated data values to columns in MS Access with by using following SQL statement: SELECT [unit_tarsus_length] AS mm
Add core information from metadata
Add core information from metadata to every unit, if missing in the unit table. You can add this information by using the SQL statement above.
Denormalise information
In the case of repeatable elements in ABCD you need to denormalise the data. For more information see the BioCASE documention Wiki - under the section "Controlled Denormalisation".
ABCD Mapping
Each column in the prepared dataset should be mapped to an ABCD element using the BioCase Provider software. There is a tutorial describing each step in the mapping under the section ABCD Mapping.